In digital content, images are not just aesthetic embellishments—they are potent tools that elevate your blog posts and significantly impact their discoverability on search engines.
The key lies in optimizing images to ensure platforms like Google and Bing understand their purpose and relevance within your blog posts.
Understanding Alt Attributes
Alt attributes, short for “alternative attributes,” are HTML attributes used within image tags () to provide a concise and descriptive text that serves as an alternative in case the image cannot be displayed. These attributes offer textual information about the content and function of the image, enabling accessibility for users with visual impairments who use screen readers. Additionally, alt attributes play a vital role in search engine optimization (SEO) by helping search engines understand and index the content of images, contributing to better overall website visibility and ranking.
Spotting Missing Alt Attributes on Your Website

Most SEO tools can alert you to the presence of images lacking alt attributes on your website. However, our tool offers a distinctive advantage – it’s free. With just a few clicks, it will comprehensively identify all images missing alt attributes, ensuring your website remains both accessible and search engine optimized.
How to do Image Alt Attributes correctly?
Adding Alt text to your images is a breeze, especially with CMS platforms like WordPress. Remember to give your images meaningful names that form a sentence with your blog.
Skip the old-style ‘0002-0003’ labels or camera-generated names. Instead, go for descriptive filenames with keywords, using hyphens between words.
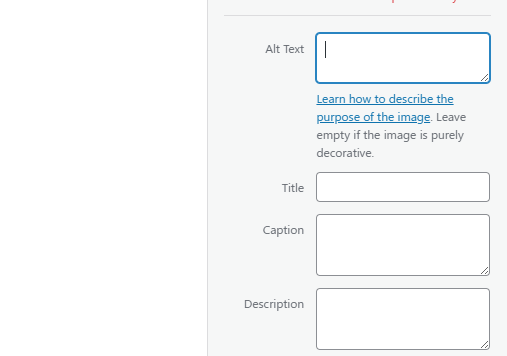
WordPress
In WordPress, find the Alt text field on the right when you select an image—as easy as that! Please keep it simple and make your pictures work smarter for better accessibility and SEO.
HTML Image Elements
Unlike CMS platforms, HTML requires a bit more understanding, especially when it comes to embedding images. Opting for standard HTML image elements is key, as it aids search engine crawlers in finding and processing images
For Example, Google effectively indexes images within HTML <img> elements, even when nested in other structures like <picture>. However, it’s crucial to note that Google doesn’t index CSS images.
Good Practice:
<img src="kitten.jpg" alt="A playful tabby kitten" />However, be cautious about opting for a less optimal approach:
Avoid:
<div style="background-image:url(kitten.jpg)">A playful tabby kitten</div>Remember, using standard HTML image elements ensures that your content gets the purr-fect attention from search engines like Google. Avoid the claws of suboptimal SEO practices and let your images shine like a content-happy cat!